Teleoperation
Remote control

Remote control
As the workforce decreases, all sorts of companies are
finding it increasingly difficult to ensure the workforce
needed for essential work, not just companies in the
construction, logistics, agriculture, and medical care
fields. The inefficiency of simple work and the fact that
only highly skilled workers can carry out sophisticated
work are serious problems in all industries. Many
automation attempts combining AI and robotics are being
made to address these challenges in recent years, but it
is not realistic in terms of technology and cost to
completely replace human flexibility and sophisticated
skills with automation.
In this context, we focused our attention on remote
control technologies. You can create cost effective work
processes by combining automation and remote manual
operations. You can automate menial tasks and perform
difficult-to-automate tasks remotely instead of trying to
automate them with a brute force approach. With the
increase in bandwidth and latency reduction of wireless
communication networks, the kinds of work that can be done
using remote control are expected to increase in the
future. intdash establishes remote control in a variety of
scenarios with excellent real-time performance and
intermediary server architecture.
Use cases

Intervention to control unmanned robots such as delivery robots and work robots in a warehouse

Remote handling of construction machines in a danger zone
Workforce reduction through consolidation of forklift and other equipment operations in the central control room
Remote support for driverless vehicles that have encountered problems
Assistance for out-of-sight flight and takeoff and landing of drones
Remote operation of avatar robot
Challenges related to remote control
For remote control, the operator creates a feedback loop with the equipment to be controlled via an operating device. This is why remote control requires incomparably better real-time performance than unidirectional data transmission. Remote control also requires stable bidirectional data fusion streaming.
- Excellent real-time feedback and bidirectional data streaming
- Integrated streaming of fusion data including control data, sensor data, and video data
- Support for control protocols specific to controlled equipment
- Fail safe mechanism that prevents uncontrolled operation in case of network disconnection
Main features of DX Functions
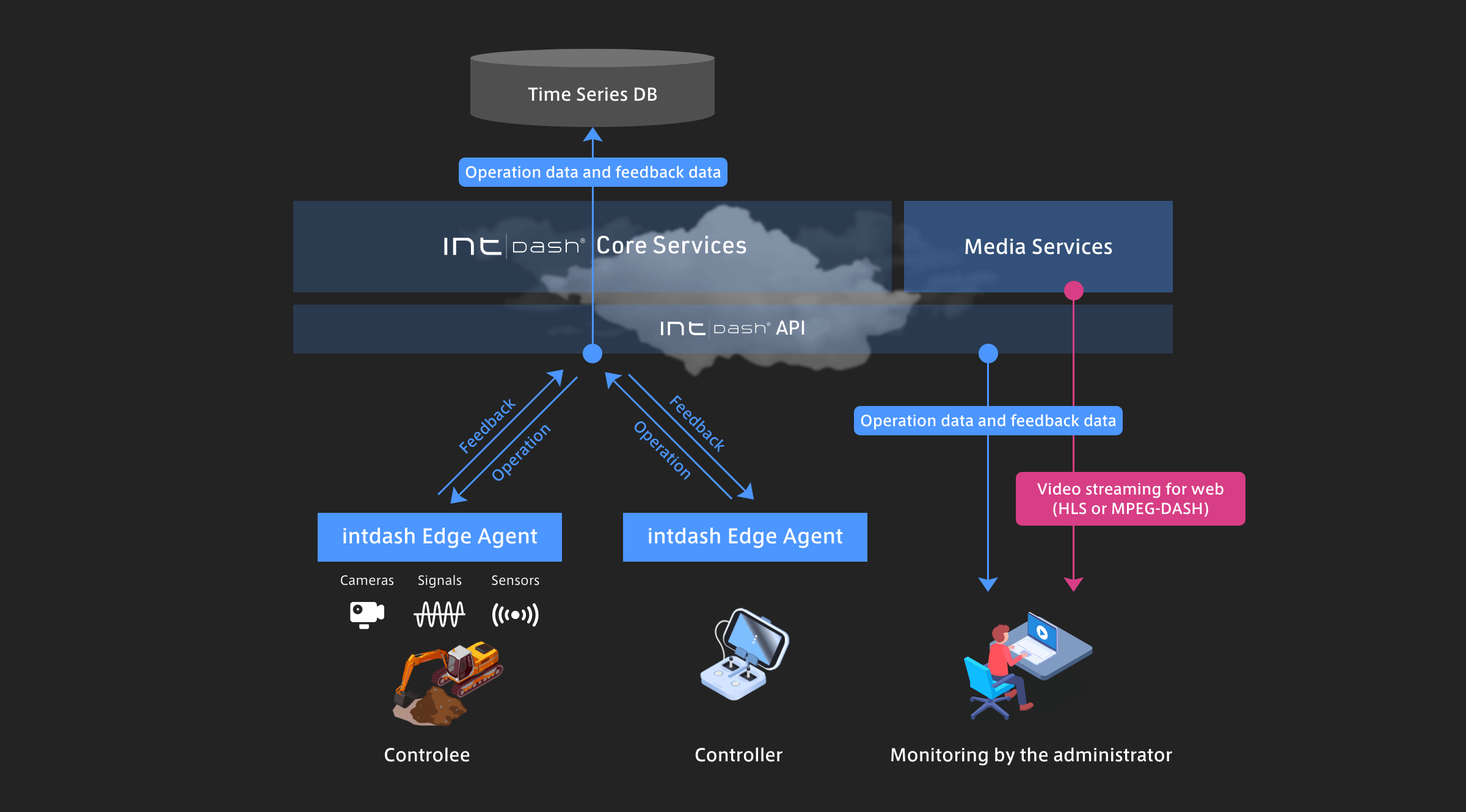
Remote control via an intermediary server
The intermediary server architecture allows for a many-to-many connection between multiple operating devices and controlled equipment.
View DetailsBidirectional streaming between operating devices and controlled equipment
Control data for operation and feedback data such as sensor signals and video are bidirectionally streamed in real time.
View DetailsFlawless collection of all live data
All data in operation sequences, including the operator's control data and response data from controlled equipment, is automatically recorded. You can use this data to develop advanced automation programs.
View DetailsLow-latency video streaming
Video data sent from edge devices can be streamed with low latency using aptpod's proprietary protocol. Video data can also be converted into HLS or WebSocket format that is easy to use in various applications.
View DetailsSupport for de facto standards in robot and drone development
Message formats widely used in robot and drone development such as ROS (Robot Operating System) and Mavlink are supported.
TELEOPERATION system reference